Lithuania
Population
3,565,000 peopleCapital
VilniusCurrency
LitasMap of Lithuania
Area in square kilometers
65,200 km2 Location of Lithuania (dark green)– on the European continent (green & dark grey)– in the European Union (green) —
Location of Lithuania (dark green)
– on the European continent (green & dark grey)
– in the European Union (green) —
During the 14th century, Lithuania was the largest country in Europe:
present-day Belarus, Ukraine, and parts of Poland and Russia were
territories of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. With the Lublin Union of
1569, Poland and Lithuania formed a new state, the Polish–Lithuanian
Commonwealth.
In the aftermath of World War I, Lithuania's Act of Independence was
signed on 16 February 1918, declaring the re-establishment of a
sovereign state. Starting in 1940, Lithuania was occupied first by the
Soviet Union and then by Nazi Germany.
Lithuania is a unitary multiparty republic with one legislative house;
its head of state is the president, and the head of government is the
prime minister. Lithuanian tribes united in the mid-13th century to
oppose the Teutonic Knights.
expanded Lithuania into an empire that dominated much of eastern
Europe in the 14th – 16th centuries. In 1386 the Lithuanian grand duke
became the king of Poland, and the two countries remained closely
associated for the next 400 years.
Lithuania, which was soon incorporated into the Soviet Union. Germany
occupied Lithuania again from 1941, but the Red Army regained control
in 1944. With the breakup of the U.S.S.R., Lithuania declared its
independence in 1990 and gained full independence in 1991.
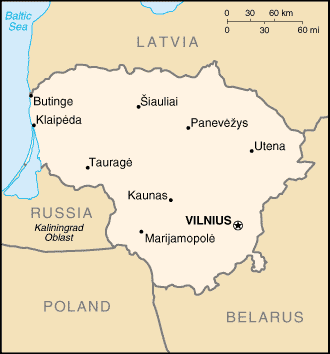
The largest and most populous of the Baltic states, Lithuania is
situated on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, in northeastern
Europe. It is bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the
southeast, Poland to the southwest, and Kaliningrad, a territory of
Russia, to the west.
and 56th latitudes and the 20th and 27th longitudes, Lithuania is
glacially flat, except for the hills (of no more than 300 meters) in
the western and eastern highlands. The terrain is marked by numerous
small lakes and swamps, and a mixed forest zone covers 30% of the
country.
Lithuanians are neither Slavic nor Germanic, although the union with
Poland and the colonization by Germans and Russians has influenced the
culture and religious beliefs of Lithuania. This highly literate
society places strong emphasis upon education, which is free and
compulsory until age 16.
Lithuania (Lietuva) is a Baltic country in Europe. It has a Baltic
Sea coastline in the west and surrounded by Latvia to the north,
Belarus to the east, Poland to the southwest, and Russia (Kaliningrad)
to the west.
Lithuania is an active member of the European Union (since 1 May 2004)
and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (since 29 March 2004).
and Eastern civilizations, Lithuania battled dramatically for its
independence and survival. Once in the Middle Ages (15th century),
Lithuania was the largest state in the entire Europe, where crafts and
overseas trade prospered.
Location of Lithuania Location of Lithuania (orange)
– on the European continent (camel white)
– in the European Union (camel)
Capital
Vilnius
54°40′N 25°19′E
Largest city
capital
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in
northern Europe.
joining the European Union, Lithuania had the highest economic growth
rate amongst all candidate and member countries, reaching 8.8 percent
in the third quarter. It became a member state of the European Union
in May 2004.
Lithuanian lands were united under MINDAUGAS in 1236; over the next
century, through alliances and conquest, Lithuania extended its
territory to include most of present-day Belarus and Ukraine. By the
end of the 14th century Lithuania was the largest state in Europe.
March 1990, Lithuania became the first of the Soviet republics to
declare its independence, but Moscow did not recognize this
proclamation until September of 1991 (following the abortive coup in
Moscow). The last Russian troops withdrew in 1993.
1898 while Lithuania was a part of Russia; it was banned during the
Soviet occupation from 1940 to 1990
Back to Top
Economy ::Lithuania
Economy - overview:
Field info displayed for all countries in alpha
Map of LithuaniaMap of Lithuania
President: Dalia Grybauskaite (2009)
Prime Minister: Gediminas Kirkilas (2006)
Total area: 25,174 sq mi (65,200 sq km)
Population (2010 est.): 3,545,319 (growth rate: –0.2%); birth rate:
9.
Lithuania Main Page
2.
The Liths, or Lithuanians, united in the 12th century under the rule
of Mindaugas, who became king in 1251. Through marriage, one of the
later Lithuanian rulers became the king of Poland (Ladislaus II) in
1386, uniting the countries.
name of Lithuania, however, did not appear in European records until
1009 AD, when it was mentioned in the German manuscript Annals of
Quedlinburg.
By the end of the 14th century, Lithuania was the largest country in
Europe, stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea.
In 1401, the formal union between Poland and Lithuania was dissolved.
While Jogaila remained the King of Poland, his cousin Grand Duke
Vytautas became the ruler of Lithuania.
* Lithuania - Coat of Arms
* Lithuania - Flag Legislation
* Lithuania - Presidential flag
* Lithuania - Minister of Defense Flag
* Lithuania - Military Flags
* Lithuania - Houseflags of Shipping Companies
* Lithuania - Yacht Club Flags
* Lithuania - Flags of High-Education Institutions
* Flags on stamps of Lithuania
Historical Flags:
has a national emblem of Lithuania in the centre of it.
Timas Pelanis, 20 October 2004
According to , the new flag law of Lithuania (since
1 Sept. 2004) set the flag ratio as 3:5 (instead of 1:2).
A virtual guide to Lithuania, the largest and most southerly of the
three Baltic republics. Get an overview of Lithuania's art, culture,
people, environment, geography, history, economy and its government.
official web sites of Lithuania, addresses of Lithuania`? and foreign
embassies, domestic airlines, local news, city- and country guides
with extensive travel and tourism information on accommodation,
tourist attractions, events and more.
Vilnius
Vilnius - old and modern © travel.
Independent between the two World Wars, Lithuania was annexed by the
USSR in 1940.
Lithuania was a powerful empire that dominated
much of eastern Europe in the 14th–16th centuries before becoming part
of the Polish-Lithuanian confederation for the next two centuries.
1990, Lithuania declared its independence by a unanimous vote of its
newly elected parliament. The new Soviet parliament acknowledged
Lithuania's independence on Sept. 6, 1991. Lithuania was admitted into
the European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization in
2004. The capital is Vilnius.
Lithuania is bounded by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and
south, Poland and the detached Russian oblast of Kaliningrad to the
southwest, and the Baltic Sea to the west.
Lithuania is the southernmost of the three Baltic states and the
largest and most populous of them. Like many countries in Eastern
Europe, Lithuania was under the authority of the Soviet Union during
the Cold War.
in Washington also want Lithuania to participate in a controversial
plan by American military planners to base anti-ballistic missiles in
Eastern Europe, in an effort to shoot down missiles fired by “rogue”
states.
Lithuanian officials have been
quiet about their country’s involvement in the missile plan.
Location of Lithuania Location of Lithuania (orange)
– on the European continent (camel & white)
– in the European Union (camel)
Capital
(and largest city)
Vilnius
Official languages
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania ( Lithuanian: Lietuvos
Respublika) is a country defined as being part of Northern Europe.
Lithuania is a member of NATO and of the European Union. Its
population is 3.4 million. The largest city and capital is Vilnius.
The Republic of Lithuania is one of the three Baltic States (the
others are Latvia and Estonia) situated on the Baltic Sea to the west
of Russia.
population of Lithuania has maintained a fairly stable percentage of
ethnic Lithuanians (from 79.3% in 1959 to 84.6% in 2006).
Written with the Latin alphabet, Lithuanian has
been the official language of Lithuania since 1989. While Lithuania
was a member of the U.S.S.R., Russian was the official language, so
many Lithuanians speak Russian as a second language.
Bar a brief interwar period of independence, Lithuania was not
independent again until 1991. Kaunas' Military Museum of Vytautas the
Great and Vilnius' National Museum cover the whole span of Lithuania's
history.
Lithuania goes back to at least 9000 BC.
The same year Lithuania was mentioned for the first time in
written sources (the Kvedlinburgh Chronicle) as the place where an
archbishop called Brunonus was struck on the head by pagans in Litae
(Latin for Lithuania).
The history of Lithuania dates back to at least 1009, the first
recorded written use of the term. Lithuanians, a branch of the
Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands, establishing the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the 13th century the short-lived
Kingdom of Lithuania.
Lithuania became the largest state in Europe through the conquest of
much of East Slav populated Ruthenia.
In 1795, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was erased from the
political map with the Partitions of the Commonwealth. Afterwards the
Lithuanians lived mostly under the rule of the Russian Empire until
the 20th century.
Lithuanian Government Information
* Government of the Republic of Lithuania
* Bank of Lithuania
* Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania
* Ministry of Finance
* Lithuanian National Commission for UNESCO (in Lithuanian only)
National office for Lithuania.
* Embassy of the Republic of Lithuania in Washington, DC
Diplomatic representation of Lithuania in the United States.
* Embassy of the United States in Vilnius, Lithuania
Diplomatic representation of the U.S. in Lithuania.
Rebellious, quirky and vibrant, Lithuania (Lietuva) is Europe's
best-kept secret.
Lithuania has an unspectacular landscape, but a vibrant culture more
than makes up for this. Of the three Soviet Baltic states of Estonia,
Latvia and Lithuania, it was the Lithuanians who made the most daring
push towards independence.
For a more mystical attraction, Lithuania's Hill of Crosses is
just the place: the thousands of crosses which cover the small hill
were hacked down several times by the Soviets, only to reappear each
time.
The ancient history of Lithuania is not much different from other
countries in the Baltic region. After the last Ice age settlements of
several tribes began to emerge.
Lithuania and European Union
Legal Education
Legal Profession
Law Libraries
Law Journals
Law Textbooks, Monographs
Law Dictionaries
Legal Publishers
Legal News
The Republic of Lithuania (Lietuvos Respublika) is an independent
democratic state. The foundation of the social system is enforced by
the Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania, adopted in 1992 by
referendum, which also establishes the rights, freedoms, and duties of
citizens.
people of Lithuania and is exercised by the Seimas (Parliament), the
President of the Republic, the Government, and the Courts. 1
The Lithuanian legal system is principally based on the legal
traditions of continental Europe.
LithuaniaCountry Specific Information
* Print
* Email
* Recent Embassy Notices for American Citizens
On this page »
* Country Description
COUNTRY DESCRIPTION: Lithuania is a stable democracy currently
experiencing the effects of the global economic downturn after years
of rapid economic growth.
Background Notes on Lithuania for additional information.
Back to Top
SMART TRAVELER ENROLLMENT PROGRAM (STEP) / EMBASSY LOCATION: If you
are going to live or visit Lithuania, please take the time to tell us
about your trip.
Lithuania,
The instrumental version of the national anthem of Lithuania.Country,
the largest of the three Baltic States, northeastern Europe.
Area: 25,212 sq mi (65,300 sq km). Population: (2010 est.) 3,297,000.
Capital: Vilnius.
Lithuania into an empire that dominated much of eastern Europe in the
14th–16th centuries. In 1386 the Lithuanian grand duke became the king
of Poland, and the two countries remained closely associated for the
next 400 years.
Lithuania again from 1941, but the Red Army regained control in 1944.
With the breakup of the U.S.S.R., Lithuania declared its independence
in 1990 and gained full independence in 1991.
map of Lithuania locator map of LithuaniaClose European Countries
* Albania
* Andorra
* Armenia
* Austria
* Azerbaijan
*
print this map print this map Lithuania description
1 | 2 Description (Page 1)
During the last Ice Age this land now called Lithuania was covered by
a thick layer of ice, and when that ice sheet retreated (or melted)
about 10,000 years ago
Lithuania was the largest country in Europe as it included present-day
Belarus, Ukraine, and significant parts of Poland.
In 1385, Lithuania's Grand Duke accepted Poland's offer to become its
king.
Book your Hotel in Lithuania online No reservation costs. Great rates
www.booking.com/Lithuania-Hotels Ad LithuaniaLithuania, Lithuanian
Lietuva, officially Republic of Lithuania, republic (2005 est. pop.
3,597,000), 25,174 sq mi (65,201 sq km), N central Europe.
Lithuania is a flatland, drained by the Nemen River. In addition to
the capital, other important cities are Kaunas, Klaipeda (Memel), and
Siauliai. About 84% of the population is Lithuanian; there are Polish,
Russian, and other minorities.
Lithuanians speak a Baltic language (see Balts), which is the official
language; Russian and Polish are also widely spoken.